Python爬虫从入门到放弃(四)requests库的基本使用
什么是requests
requests是基于上篇的urllib编写的,采用的是Apache2 Licensed开源协议的HTTP库
如果你看过上篇文章关于urllib库的使用,你会发现,其实urllib还是非常不方便的,而requests它会比urllib更加方便,可以节约我们大量的工作。(用了requests之后,你基本都不愿意用urllib了)一句话,requests是python实现的最简单易用的HTTP库,建议爬虫使用requests库。
默认安装好python之后,是没有安装requests模块的,需要单独通过pip安装
1 | pip install -U requests |
requests功能详解
总体功能的一个演示
1 | import requests |
我们可以看出response使用起来确实非常方便,这里有个问题需要注意一下:
很多情况下的网站如果直接response.text会出现乱码的问题,所以这个使用response.content
这样返回的数据格式其实是二进制格式,然后通过decode()转换为utf-8,这样就解决了通过response.text直接返回显示乱码的问题.
请求发出后,requests会基于HTTP头部对响应的编码作出有根据的推测。当你访问response.text之时,requests会使用其推测的文本编码。你可以找出requests使用了什么编码,并且能够使用response.encoding属性来改变它.如:
1 | response =requests.get("http://www.baidu.com") |
不管是通过response.content.decode("utf-8)的方式还是通过response.encoding="utf-8"的方式都可以避免乱码的问题发生
各种请求方式
requests里提供个各种请求方式
1 | import requests |
基本GET请求
1 | import requests |
带参数的GET请求,例子1
1 | import requests |
如果我们想要在URL查询字符串传递数据,通常我们会通过httpbin.org/get?key=val方式传递。requests模块允许使用params关键字传递参数,以一个字典来传递这些参数,例子如下:
1 | import requests |
解析json
1 | import requests |
从结果可以看出两者的返回是一样的,阅读源码发现requests里面集成的json其实就是执行了json.loads()方法,两者的结果是一样的
获取二进制数据
在上面提到了response.content,这样获取的数据是二进制数据,同样的这个方法也可以用于下载图片以及
视频资源
添加headers
和前面我们将urllib模块的时候一样,我们同样可以定制headers的信息,如当我们直接通过requests请求知乎网站的时候,默认是无法访问的
1 | import requests |
这样会得到如下的错误
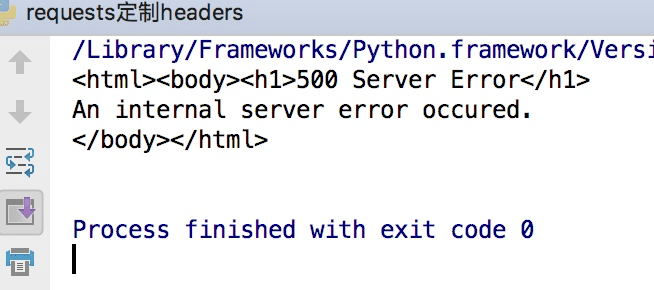
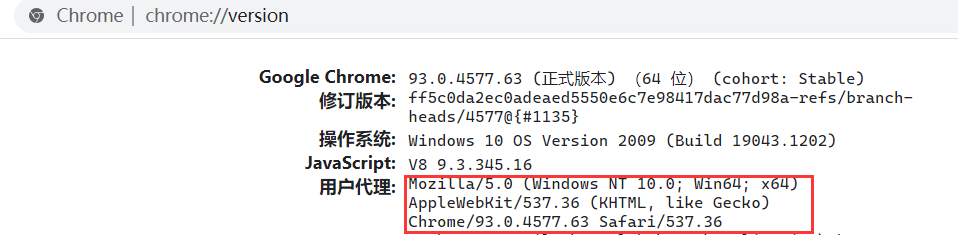
因为访问知乎需要头部信息,这个时候我们在谷歌浏览器里输入chrome://version,就可以看到用户代理,将用户代理添加到头部信息
1 | import requests |
这样就可以正常的访问知乎了
基本POST请求
通过在发送post请求时添加一个data参数,这个data参数可以通过字典构造成,这样对于发送post请求就非常方便
1 | import requests |
同样的在发送post请求的时候也可以和发送get请求一样通过headers参数传递一个字典类型的数据
响应
我们可以通过response获得很多属性,例子如下
1 | import requests |

状态码判断
requests还附带了一个内置的状态码查询对象,主要有如下内容:
1 | 100: ('continue',), |
通过下面例子测试:(不过通常还是通过状态码判断更方便)
1 | import requests |
requests高级用法
文件上传
实现方法和其他参数类似,也是构造一个字典然后通过files参数传递
1 | import requests |
结果如下:
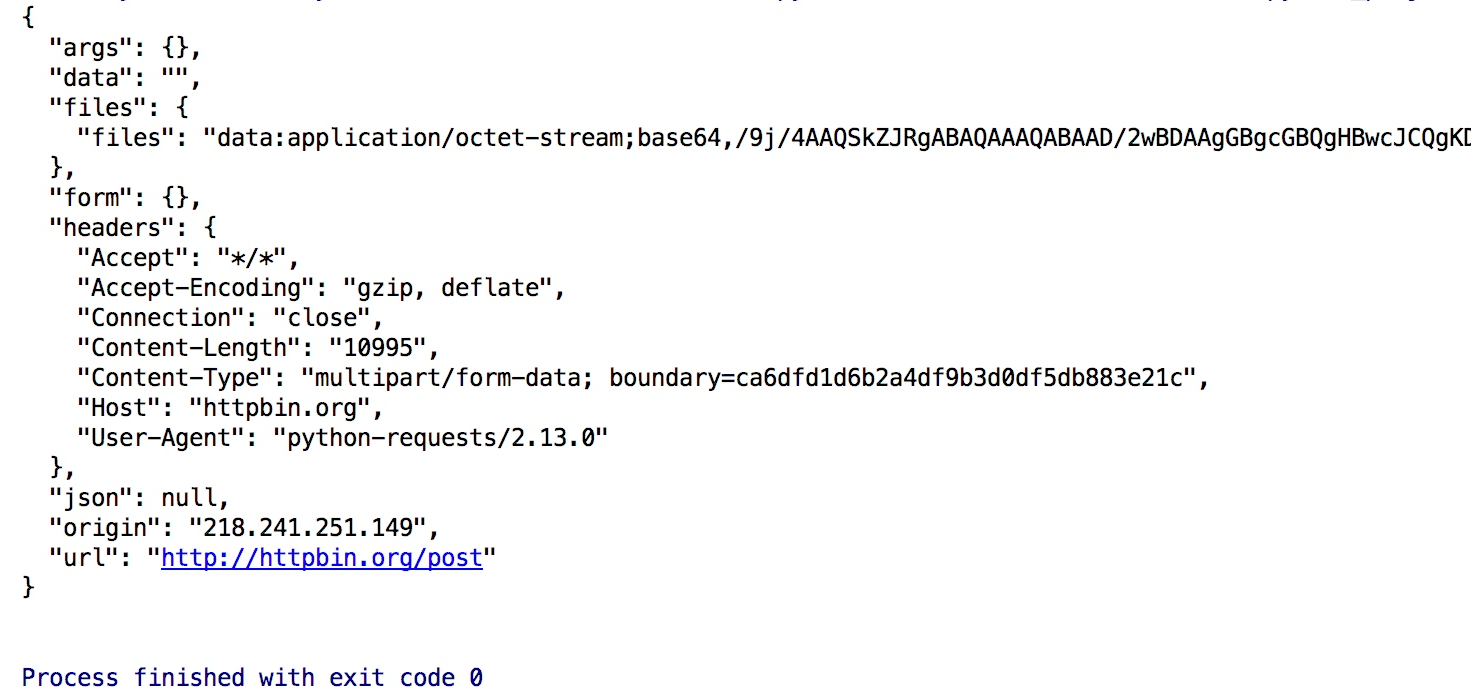
获取cookie
1 | import requests |
会话维持
cookie的一个作用就是可以用于模拟登陆,做会话维持
1 | import requests |
这是正确的写法,而下面的写法则是错误的
1 | import requests |
因为这种方式是两次requests请求之间是独立的,而第一次则是通过创建一个session对象,两次请求都通过这个对象访问
证书验证
现在的很多网站都是https的方式访问,所以这个时候就涉及到证书的问题
1 | import requests |
默认的12306网站的证书是不合法的,这样就会提示如下错误
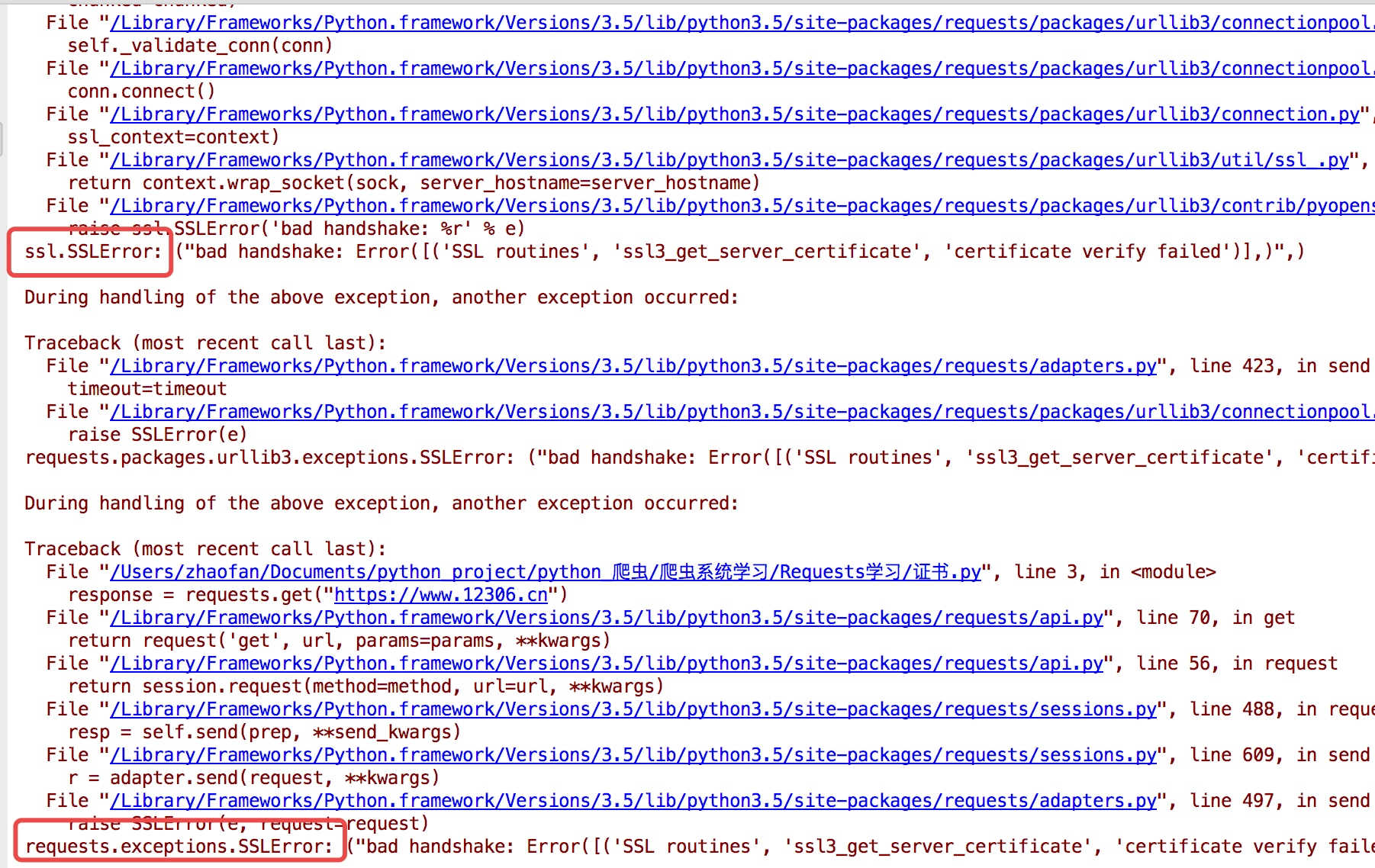
为了避免这种情况的发生可以通过verify=False
虽然这样可以访问到页面,但是会提示:
InsecureRequestWarning: Unverified HTTPS request is being made. Adding certificate verification is strongly advised.
See: https://urllib3.readthedocs.io/en/latest/advanced-usage.html#ssl-warnings InsecureRequestWarning)
解决方法为:
1 | import requests |
这样就不会提示警告信息,当然也可以通过cert参数放入证书路径
代理设置
1 | import requests |
如果代理需要设置账户名和密码,只需要将字典更改为如下:
1 | proxies = { |
如果你的代理是通过socks这种方式则需要pip install requests[socks]
1 | proxies= { |
超时设置
通过timeout参数可以设置超时的时间
认证设置
如果碰到需要认证的网站可以通过requests.auth模块实现
1 | import requests |
当然这里还有一种方式
1 | import requests |
异常处理
关于requests的异常在这里可以看到详细内容:
https://docs.python-requests.org/en/latest/api/#exceptions
所有的异常都是在requests.exceptions中

从源码我们可以看出RequestException继承IOError,HTTPError,ConnectionError,Timeout继承RequestExceptionProxyError,SSLError继承ConnectionErrorReadTimeout继承Timeout异常
这里列举了一些常用的异常继承关系,详细的可以看:
https://docs.python-requests.org/en/master/_modules/requests/exceptions/#RequestException
通过下面的例子进行简单的演示
1 | import requests |
其实最后测试可以发现,首先被捕捉的异常是timeout,当把网络断掉的haul就会捕捉到ConnectionError,如果前面异常都没有捕捉到,最后也可以通过RequestException捕捉到
最后
这里只是简单介绍基本操作,高级操作请look官方文档。